1. Boosting Cross-Border Trade
The Kurdistan Region has made significant strides in expanding cross-border trade, especially with neighboring countries like Turkey, Iran, and Iraq. Increased customs cooperation and infrastructure improvements have facilitated smoother trade flows, making Kurdistan an attractive trade hub.
2. Expanding Export Markets
Kurdistan’s export economy has seen growth in oil, agricultural products, and consumer goods. Efforts to tap into new export markets in the Middle East and beyond are paying off, with trade agreements opening doors to international buyers and reducing reliance on traditional markets.
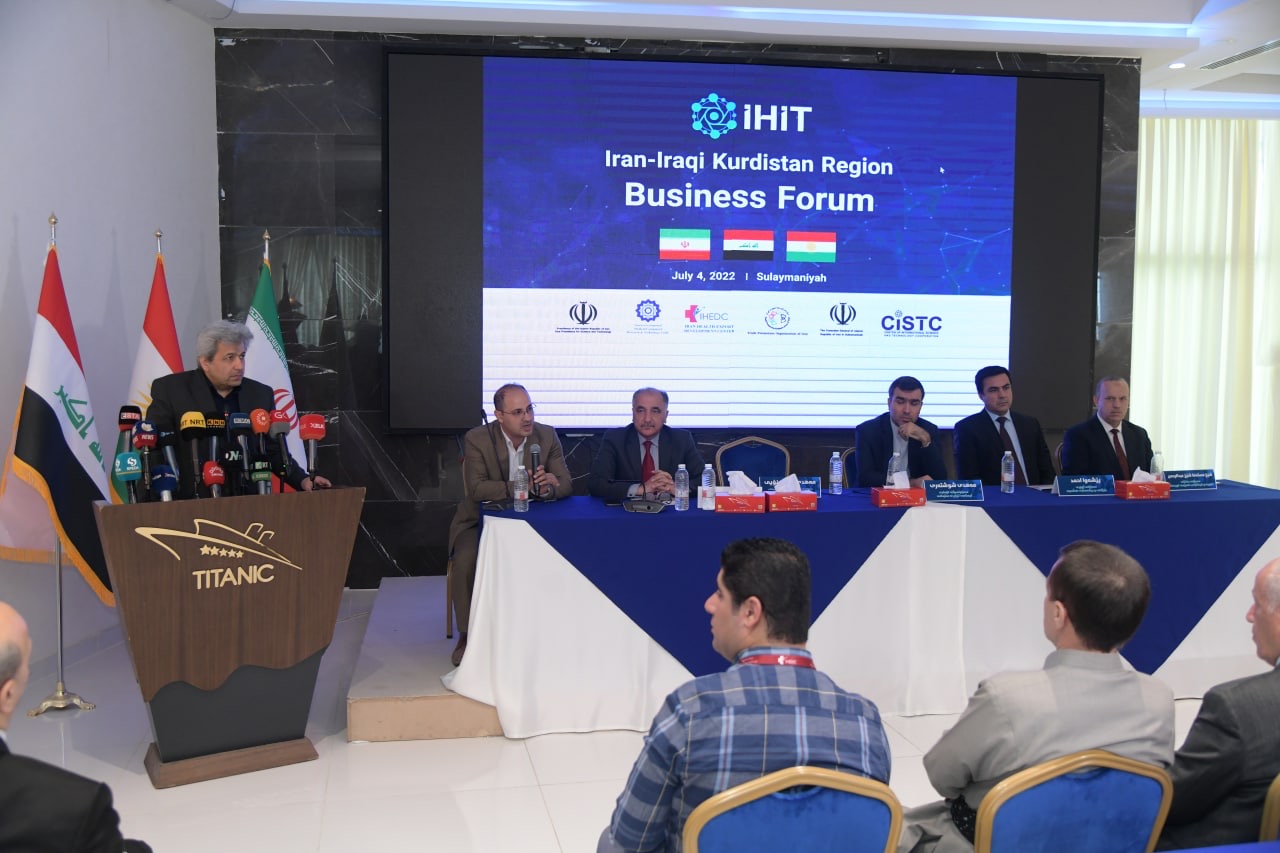

3. Focus on Non-Oil Exports
While oil remains a dominant export, the Kurdistan Region is making concerted efforts to diversify its export base. Agriculture, food processing, textiles, and handicrafts are becoming increasingly important in boosting non-oil exports, supported by government initiatives and incentives for local producers.
4. Trade Challenges and Solutions
Kurdistan faces several challenges in trade, including border delays, currency fluctuations, and political instability. To overcome these, the KRG is investing in improving trade infrastructure, simplifying regulations, and establishing economic partnerships with key international players.
5. The Future of Trade in Kurdistan
With expanding trade routes and investment in infrastructure, Kurdistan’s future in international trade looks promising. The KRG is also focusing on digital trade solutions and logistics innovations to streamline processes and reduce trade barriers, enabling a more competitive export sector.





